Alcalá S, Villarino L, Ruiz L, Couceiro JR, Martínez M, Palencia A, Navarro D, Cabezas P, Rodriguez I, Cordero A, Trilla L, Rubiolo JA, Batres S, Vallespinos M, González C, Rodríguez J, Gámez A, Vara J, Fernández SF, Berlinches AB, Moreno N, Redondo A, Carrato A, Hermann PC, Sánchez L, Torrente S, Fernández MÁ, Mascareñas JL, Sainz BJR. Targeting cancer stem cell OXPHOS with tailored ruthenium complexes as a new anti-cancer strategy
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024
"We hope to further develop Ru1 and analogues into clinically-available therapies to treat CSC-driven tumors, like pancreatic cancer, an essentially incurable cancer". - Bruno Sainz Anding
Summary:
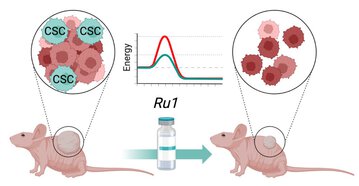
The main result of this publication is that Ru1 is capable of inhibiting CSC OXPHOS function in vitro, and more importantly, it presents excellent anti-cancer activity, with low toxicity, across a large panel of human pancreatic PDXs, as well as in colorectal cancer and osteosarcoma PDXs. Mechanistic studies suggest that this activity stems from Ru1 binding to the D-loop region of the mitochondrial DNA of CSCs, inhibiting OXPHOS complex-associated transcription, leading to reduced mitochondrial oxygen consumption, membrane potential, and ATP production, all of which are necessary for CSCs, which heavily depend on mitochondrial respiration.
Overall, the coordination complex Ru1 represents not only an exciting new anti-cancer agent, but also a molecular tool to dissect the role of OXPHOS in CSCs. Results indicating that the compound is safe, non-toxic and highly effective in vivo are extremely exciting, and have allowed us to uncover unprecedented mechanistic possibilities to fight different cancer types based on targeting CSC OXPHOS.
Why do you highlight this publication?
In this study we describe a new metal-based compound (known as Ru1) that targets mitochondrial respiration of cancer stem cells (CSCs), decreasing their tumor-generating potential. CSCs rely on mitochondrial respiration to meet their energy requirements, which highlights a targetable vulnerability to treat different types of cancer, like pancreatic cancer. We provide extensive pre-clinical evidence to demonstrate the safetty and anti-CSC capacity of Ru1 across numerous patient-derived xenograft models. The project is currently at an advanced stage for its transfer and preclinical valorization, thanks to the support of different entities, including the Ignicia program of the Xunta de Galicia, the AECC, and the CaixaImpulse program ("la Caixa" Foundation).
Publication commented by:
Dr. Bruno Sainz Anding
BIOMARKERS AND PERSONALIZED APPROACH TO CANCER (BIOPAC) GROUP – IRYCIS