Kirk B, Cawthon PM, Arai H,..., Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Global Leadership Initiative in Sarcopenia (GLIS) group. The Conceptual Definition of Sarcopenia: Delphi Consensus from the Global Leadership Initiative in Sarcopenia (GLIS)
Age Ageing. 2024
“This is the first global consensus definition of sarcopenia" - AJ Cruz Jentoft
Summary:
Importance: Sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass and strength/function, is an important clinical condition. However, no international consensus on the definition exists.
Objective: The Global Leadership Initiative in Sarcopenia (GLIS) aimed to address this by establishing the global conceptual definition of sarcopenia.
Design: The GLIS steering committee was formed in 2019-21 with representatives from all relevant scientific societies worldwide. During this time, the steering committee developed a set of statements on the topic and invited members from these societies to participate in a two-phase International Delphi Study. Between 2022 and 2023, participants ranked their agreement with a set of statements using an online survey tool (SurveyMonkey). Statements were categorised based on predefined thresholds: strong agreement (>80%), moderate agreement (70-80%) and low agreement (<70%). Statements with strong agreement were accepted, statements with low agreement were rejected and those with moderate agreement were reintroduced until consensus was reached.
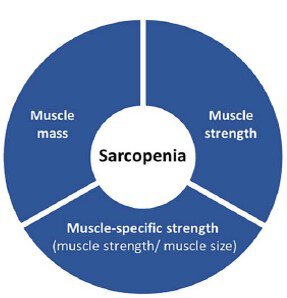
Results: 107 participants (mean age: 54 ± 12 years [1 missing age], 64% men) from 29 countries across 7 continents/regions completed the Delphi survey. Twenty statements were found to have a strong agreement. These included; 6 statements on 'general aspects of sarcopenia' (strongest agreement: the prevalence of sarcopenia increases with age (98.3%)), 3 statements on 'components of sarcopenia' (muscle mass (89.4%), muscle strength (93.1%) and muscle-specific strength (80.8%) should all be a part of the conceptual definition of sarcopenia)) and 11 statements on 'outcomes of sarcopenia' (strongest agreement: sarcopenia increases the risk of impaired physical performance (97.9%)). A key finding of the Delphi survey was that muscle mass, muscle strength and muscle-specific strength were all accepted as 'components of sarcopenia', whereas impaired physical performance was accepted as an 'outcome' rather than a 'component' of sarcopenia.
Conclusion and relevance: The GLIS has created the first global conceptual definition of sarcopenia, which will now serve to develop an operational definition for clinical and research settings.
Why do you highlight this publication?
There are currently several definitions of sarcopenia in use around the world, using different parameters to define the condition. The GLIS initiative has been able to bring together all the working groups (Europe, Asia, America and Australia-New Zealand) to produce a first global definition of sarcopenia. This conceptual definition will allow a consensus operational definition, which is currently under development, to be used worldwide, thereby facilitating its translation into mainstream clinical care.
Publication commented by:
Dr. Cruz-Jentoft
Geriatry Department, Head. HURYC
Geriatrics group, IRYCIS